Peering into the Minuscule World: How Does a Digital Microscope Work?
The evolution in microscopy has led to an intriguing question; how does a digital microscope work? This technological marvel provides unprecedented insights into minute worlds that remain hidden from our naked eyes.
This article illuminates the inner workings of digital microscopes, focusing on their unique features, operation principles, and potential applications. Let’s dive deeper!
Digital Microscopy: The Intersection of Optics and Electronics

At its core, digital microscopy blends traditional optics with modern electronics. Its primary component is an optical lens system that magnifies tiny objects onto an electronic sensor instead of your eye.
The result? High-resolution images displayed directly on computer screens or touchscreens for detailed analysis—a significant leap from conventional microscopes requiring eyepiece peering.
Digital Microscopes: How Do They Capture Images?
A key aspect when understanding how does a digital microscope work lies in image capture mechanics. Unlike traditional counterparts relying solely on light reflection or transmission through specimens, these devices use sensors to convert optical information into electronic signals—creating digitized images ready for viewing or further processing.
In-Depth Look at Image Processing Capabilities

Another crucial aspect of how does a digital microscope work is its image processing capabilities. This feature allows users to manipulate images, enhance details, and even measure microscopic elements with precision.
The 1200X Touchscreen Digital Microscope, for instance, boasts triple cameras offering different perspectives—enabling comprehensive analysis of specimens under scrutiny.
Benefits & Applications: Why Choose Digital Microscopy?
Digital microscopy offers numerous advantages over traditional methods. From high-resolution imaging to advanced image processing features—these devices are revolutionizing various fields like research, education, forensics, medicine among others.
Their ability to record videos also opens up dynamic study possibilities that static images can’t provide. It’s no wonder many professionals prefer them!
How Does a Digital Microscope Work: Maximizing Your Digital Microscopy Experience
To get the most out of your digital microscope experience; proper handling and understanding your device’s unique features is key. For example, adjusting lighting conditions or utilizing the zoom function can significantly improve image quality.
Digital Microscopes: A Glimpse into Future Trends
Innovation never stops in the realm of microscopy! With advancements in sensor technology and artificial intelligence algorithms—future trends promise even more exciting developments in this field.
Explore our 1200X Touchscreen Digital Microscope today!
Understanding the Intricacies: How Does a Digital Microscope Work?
The workings of a digital microscope revolve around several key components. The light source illuminates the specimen, which is then magnified by an objective lens.
This image passes through a tube where it’s directed onto an electronic sensor or camera instead of your eye. This sensor converts optical signals into electronic ones, creating digital images that can be displayed on screens for detailed examination.
How Does a Digital Microscope Work: A Leap in Image Resolution
A significant advantage of using digital microscopes lies in their ability to offer high-resolution imaging. This means they can produce highly detailed pictures with excellent clarity and sharpness—making them ideal tools for scientific research, medical diagnosis, and industrial inspection among others.
Diving Deeper Into Image Processing Functions
Beyond capturing images, how does a digital microscope work when it comes to processing these visuals? These devices are equipped with software that enables users to analyze and manipulate captured images digitally.
You can zoom in on specific areas, adjust brightness or contrast levels, add annotations—essentially transforming raw data into valuable insights!
How Does a Digital Microscope Work: Why Go Digital?
Moving from traditional to digital microscopy brings forth numerous benefits. Besides superior image quality and advanced analysis capabilities—they also allow easy sharing and storage of information—a boon in collaborative environments like laboratories or classrooms.
In addition—their compact design makes them portable while touchscreen interfaces enhance user-friendliness.
Maximizing Efficiency: Tips for Using Digital Microscopes
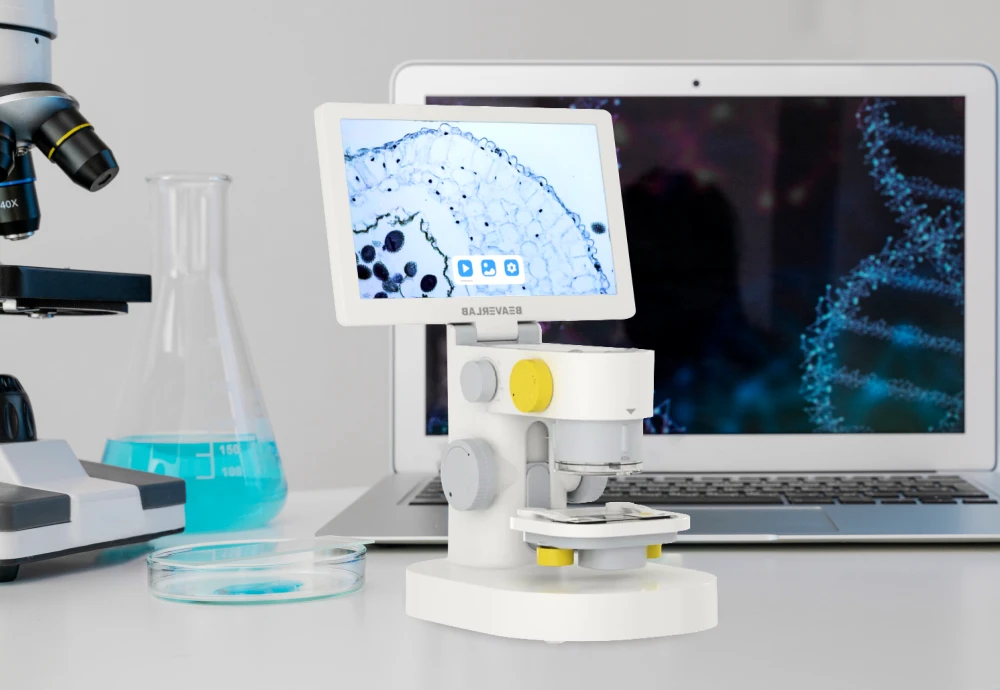
To optimize your digital microscopy experience, understanding your device’s unique features is crucial. For instance—knowing how to adjust lighting conditions or the zoom function can significantly improve image quality and analysis accuracy.
















Leave a comment